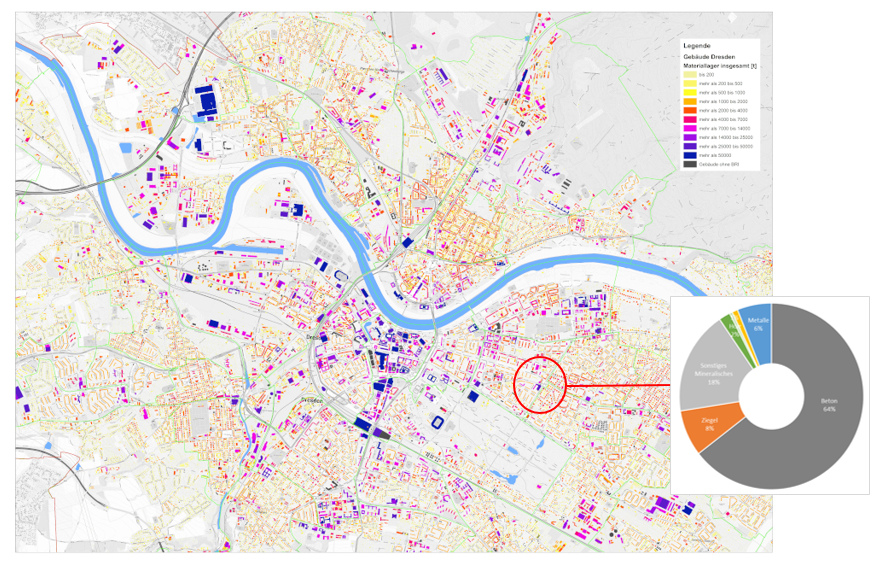
Material cadastres describe the material stocks of existing buildings (residential and non-residential) and infrastructures (streets and roads).
Material stocks continues to increase in Germany and is transforming in its make-up. Knowledge in this regard comprises a significant foundation for estimation of material flows and potential for the recycling economy in the construction sector.
Material cadastres are created by cities or regions and provide important information about how these can be developed in a more circular fashion.
First, the quantity framework of existing buildings and roads is determined. It takes into account type-based differentiations. For residential buildings, the differentiations are generated by age of the construction, for non-residential buildings by use, and for roads by size categories. The units of measure are cubic metre or square metre (m³ or m²) for buildings and metre or square metre for roads. The quantity structure is based on factual data (e.g. building statistics) and geodata (LoD1 in combination with ALKIS).
Pursuant the typological differentiations, the material composition indicators (MCI) for buildings and streets are then determined. They provide information regarding which and how much material is contained (for example) in a m³ (cubic metre) building and/or a m² (sq. m.) street. These MCI for buildings and infrastructures can be downloaded here in the information system.